TWIS — I2C compatible two-wire interface slave with EasyDMA
TWI slave with EasyDMA (TWIS) is compatible with I2C operating at 100 kHz and 400 kHz. The TWI transmitter and receiver implement EasyDMA.
A typical TWI setup consists of one master and one or more slaves. For an example, see Figure 2. TWIS is only able to operate with a single master on the TWI bus.
The TWI slave state machine is illustrated in Figure 3 and Table 1 is explaining the different symbols used in the state machine.
| Symbol | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| ENABLE | Register | The TWI slave has been enabled via the ENABLE register |
| PREPARETX | Task | The TASKS_PREPARETX task has been triggered |
| STOP | Task | The TASKS_STOP task has been triggered |
| PREPARERX | Task | The TASKS_PREPARERX task has been triggered |
| STOPPED | Event | The EVENTS_STOPPED event was generated |
| RXSTARTED | Event | The EVENTS_RXSTARTED event was generated |
| TXSTARTED | Event | The EVENTS_TXSTARTED event was generated |
| TX prepared | Internal | Internal flag indicating that a TASKS_PREPARETX task has been triggered. This flag is not visible to the user. |
| RX prepared | Internal | Internal flag indicating that a TASKS_PREPARERX task has been triggered. This flag is not visible to the user. |
| Unprepare TX | Internal | Clears the internal 'TX prepared' flag until next TASKS_PREPARETX task. |
| Unprepare RX | Internal | Clears the internal 'RX prepared' flag until next TASKS_PREPARERX task. |
| Stop sequence | TWI protocol | A TWI stop sequence was detected |
| Restart sequence | TWI protocol | A TWI restart sequence was detected |
The TWI slave supports clock stretching performed by the master.
The TWI slave operates in a low power mode while waiting for a TWI master to initiate a transfer. As long as the TWI slave is not addressed, it will remain in this low power mode.
To secure correct behaviour of the TWI slave, PSEL.SCL, PSEL.SDA, CONFIG and the ADDRESS[n] registers, must be configured prior to enabling the TWI slave through the ENABLE register. Similarly, changing these settings must be performed while the TWI slave is disabled. Failing to do so may result in unpredictable behaviour.
Shared resources
The TWI slave shares registers and other resources with other peripherals that have the same ID as the TWI slave.
Therefore, you must disable all peripherals that have the same ID as the TWI slave before the TWI slave can be configured and used. Disabling a peripheral that has the same ID as the TWI slave will not reset any of the registers that are shared with the TWI slave. It is therefore important to configure all relevant registers explicitly to secure that the TWI slave operates correctly.
The Instantiation table in Instantiation shows which peripherals have the same ID as the TWI slave.
EasyDMA
The TWI slave implements EasyDMA for reading and writing to and from the RAM.
The STOPPED event indicates that EasyDMA has finished accessing the buffer in RAM.
If the TXD.PTR and the RXD.PTR are not pointing to the Data RAM region, an EasyDMA transfer may result in a HardFault or RAM corruption. See Memory for more information about the different memory regions.
TWI slave responding to a read command
Before the TWI slave can respond to a read command the TWI slave must be configured correctly and enabled via the ENABLE register. When enabled the TWI slave will be in its IDLE state where it will consume IIDLE .
A read command is started when the TWI master generates a start condition on the TWI bus, followed by clocking out the address and the READ/WRITE bit set to 1 (WRITE=0, READ=1). The READ/WRITE bit is followed by an ACK/NACK bit (ACK=0 or NACK=1) response from the TWI slave.
The TWI slave is able to listen for up to two addresses at the same time. Which addresses to listen for is configured in the ADDRESS registers and the CONFIG register.
The TWI slave will only acknowledge (ACK) the read command if the address presented by the master matches one of the addresses the slave is configured to listen for. The TWI slave will generate a READ event when it acknowledges the read command.
The TWI slave is only able to detect a read command from the IDLE state.
The TWI slave will set an internal 'TX prepared' flag when the PREPARETX task is triggered.
When the read command is received the TWI slave will enter the TX state if the internal 'TX prepared' flag is set.
If the internal 'TX prepared' flag is not set when the read command is received, the TWI slave will stretch the master's clock until the PREPARETX task is triggered and the internal 'TX prepared' flag is set.
The TWI slave will generate the TXSTARTED event and clear the 'TX prepared' flag ('unprepare TX') when it enters the TX state. In this state the TWI slave will send the data bytes found in the transmit buffer to the master using the master's clock. The TWI slave will consume ITX in this mode.
The TWI slave will go back to the IDLE state if the TWI slave receives a restart command when it is in the TX state.
The TWI slave is stopped when it receives the stop condition from the TWI master. A STOPPED event will be generated when the transaction has stopped. The TWI slave will clear the 'TX prepared' flag ('unprepare TX') and go back to the IDLE state when it has stopped.
The transmit buffer is located in RAM at the address specified in the TXD.PTR register. The TWI slave will only be able to send TXD.MAXCNT bytes from the transmit buffer for each transaction. If the TWI master forces the slave to send more than TXD.MAXCNT bytes, the slave will send the byte specified in the ORC register to the master instead. If this happens, an ERROR event will be generated.
The EasyDMA configuration registers, see TXD.PTR etc., are latched when the TXSTARTED event is generated.
The TWI slave can be forced to stop by triggering the STOP task. A STOPPED event will be generated when the TWI slave has stopped. The TWI slave will clear the 'TX prepared' flag and go back to the IDLE state when it has stopped, see also Terminating an ongoing TWI transaction.
Each byte sent from the slave will be followed by an ACK/NACK bit sent from the master. The TWI master will generate a NACK following the last byte that it wants to receive to tell the slave to release the bus so that the TWI master can generate the stop condition. The TXD.AMOUNT register can be queried after a transaction to see how many bytes were sent.
A typical TWI slave read command response is illustrated in Figure 4. Occurrence 2 in the figure illustrates clock stretching performed by the TWI slave following a SUSPEND task.
TWI slave responding to a write command
Before the TWI slave can respond to a write command the TWI slave must be configured correctly and enabled via the ENABLE register. When enabled the TWI slave will be in its IDLE state where it will consume IIDLE.
A write command is started when the TWI master generates a start condition on the TWI bus, followed by clocking out the address and the READ/WRITE bit set to 0 (WRITE=0, READ=1). The READ/WRITE bit is followed by an ACK/NACK bit (ACK=0 or NACK=1) response from the slave.
The TWI slave is able to listen for up to two addresses at the same time. Which addresses to listen for is configured in the ADDRESS registers and the CONFIG register.
The TWI slave will only acknowledge (ACK) the write command if the address presented by the master matches one of the addresses the slave is configured to listen for. The TWI slave will generate a WRITE event if it acknowledges the write command.
The TWI slave is only able to detect a write command from the IDLE state.
The TWI slave will set an internal 'RX prepared' flag when the PREPARERX task is triggered.
When the write command is received the TWI slave will enter the RX state if the internal 'RX prepared' flag is set.
If the internal 'RX prepared' flag is not set when the write command is received, the TWI slave will stretch the master's clock until the PREPARERX task is triggered and the internal 'RX prepared' flag is set.
The TWI slave will generate the RXSTARTED event and clear the internal 'RX prepared' flag ('unprepare RX') when it enters the RX state. In this state the TWI slave will be able to receive the bytes sent by the TWI master. The TWI slave will consume IRX in this mode.
The TWI slave will go back to the IDLE state if the TWI slave receives a restart command when it is in the RX state.
The TWI slave is stopped when it receives the stop condition from the TWI master. A STOPPED event will be generated when the transaction has stopped. The TWI slave will clear the internal 'RX prepared' flag ('unprepare RX') and go back to the IDLE state when it has stopped.
The receive buffer is located in RAM at the address specified in the TXD.PTR register. The TWI slave will only be able to receive as many bytes as specified in the RXD.MAXCNT register. If the TWI master tries to send more bytes to the slave than the slave is able to receive,these bytes will be discarded and the bytes will be NACKed by the slave. If this happens, an ERROR event will be generated.
The EasyDMA configuration registers, see RXD.PTR etc., are latched when the RXSTARTED event is generated.
The TWI slave can be forced to stop by triggering the STOP task. A STOPPED event will be generated when the TWI slave has stopped. The TWI slave will clear the internal 'RX prepared' flag and go back to the IDLE state when it has stopped, see also Terminating an ongoing TWI transaction.
The TWI slave will generate an ACK after every byte received from the master. The RXD.AMOUNT register can be queried after a transaction to see how many bytes were received.
A typical TWI slave write command response is illustrated in Figure 5. Occurrence 2 in the figure illustrates clock stretching performed by the TWI slave following a SUSPEND task.
Master repeated start sequence
An example of a repeated start sequence is one in which the TWI master writes two bytes to the slave followed by reading four bytes from the slave.
This is illustrated in Figure 6.
It is here assumed that the receiver does not know in advance what the master wants to read, and that this information is provided in the first two bytes received in the write part of the repeated start sequence. To guarantee that the CPU is able to process the received data before the TWI slave starts to reply to the read command, the SUSPEND task is triggered via a shortcut from the READ event generated when the read command is received. When the CPU has processed the incoming data and prepared the correct data response, the CPU will resume the transaction by triggering the RESUME task.
Terminating an ongoing TWI transaction
In some situations, e.g. if the external TWI master is not responding correctly, it may be required to terminate an ongoing transaction.
This can be achieved by triggering the STOP task. In this situation a STOPPED event will be generated when the TWI has stopped independent of whether or not a STOP condition has been generated on the TWI bus. The TWI slave will release the bus when it has stopped and go back to its IDLE state.
Low power
When putting the system in low power and the peripheral is not needed, lowest possible power consumption is achieved by stopping, and then disabling the peripheral.
The STOP task may not be always needed (the peripheral might already be stopped), but if it is sent, software shall wait until the STOPPED event was received as a response before disabling the peripheral through the ENABLE register.
Slave mode pin configuration
The SCL and SDA signals associated with the TWI slave are mapped to physical pins according to the configuration specified in the PSEL.SCL and PSEL.SDA registers respectively.
The PSEL.SCL and PSEL.SDA registers and their configurations are only used as long as the TWI slave is enabled, and retained only as long as the device is in ON mode. When the peripheral is disabled, the pins will behave as regular GPIOs, and use the configuration in their respective OUT bit field and PIN_CNF[n] register. PSEL.SCL and PSEL.SDA must only be configured when the TWI slave is disabled.
To secure correct signal levels on the pins used by the TWI slave when the system is in OFF mode, and when the TWI slave is disabled, these pins must be configured in the GPIO peripheral as described in Table 2.
Only one peripheral can be assigned to drive a particular GPIO pin at a time. Failing to do so may result in unpredictable behavior.
| TWI slave signal | TWI slave pin | Direction | Output value | Drive strength |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| SCL | As specified in PSEL.SCL | Input | Not applicable | S0D1 |
| SDA | As specified in PSEL.SDA | Input | Not applicable | S0D1 |
Registers
| Base address | Peripheral | Instance | Description | Configuration | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0x40003000 | TWIS | TWIS0 |
Two-wire interface slave 0 |
||
| 0x40004000 | TWIS | TWIS1 |
Two-wire interface slave 1 |
||
| Register | Offset | Description | |
|---|---|---|---|
| TASKS_STOP | 0x014 |
Stop TWI transaction |
|
| TASKS_SUSPEND | 0x01C |
Suspend TWI transaction |
|
| TASKS_RESUME | 0x020 |
Resume TWI transaction |
|
| TASKS_PREPARERX | 0x030 |
Prepare the TWI slave to respond to a write command |
|
| TASKS_PREPARETX | 0x034 |
Prepare the TWI slave to respond to a read command |
|
| EVENTS_STOPPED | 0x104 |
TWI stopped |
|
| EVENTS_ERROR | 0x124 |
TWI error |
|
| EVENTS_RXSTARTED | 0x14C |
Receive sequence started |
|
| EVENTS_TXSTARTED | 0x150 |
Transmit sequence started |
|
| EVENTS_WRITE | 0x164 |
Write command received |
|
| EVENTS_READ | 0x168 |
Read command received |
|
| SHORTS | 0x200 |
Shortcut register |
|
| INTEN | 0x300 |
Enable or disable interrupt |
|
| INTENSET | 0x304 |
Enable interrupt |
|
| INTENCLR | 0x308 |
Disable interrupt |
|
| ERRORSRC | 0x4D0 |
Error source |
|
| MATCH | 0x4D4 |
Status register indicating which address had a match |
|
| ENABLE | 0x500 |
Enable TWIS |
|
| PSEL.SCL | 0x508 |
Pin select for SCL signal |
|
| PSEL.SDA | 0x50C |
Pin select for SDA signal |
|
| RXD.PTR | 0x534 |
RXD Data pointer |
|
| RXD.MAXCNT | 0x538 |
Maximum number of bytes in RXD buffer |
|
| RXD.AMOUNT | 0x53C |
Number of bytes transferred in the last RXD transaction |
|
| TXD.PTR | 0x544 |
TXD Data pointer |
|
| TXD.MAXCNT | 0x548 |
Maximum number of bytes in TXD buffer |
|
| TXD.AMOUNT | 0x54C |
Number of bytes transferred in the last TXD transaction |
|
| ADDRESS[0] | 0x588 |
TWI slave address 0 |
|
| ADDRESS[1] | 0x58C |
TWI slave address 1 |
|
| CONFIG | 0x594 |
Configuration register for the address match mechanism |
|
| ORC | 0x5C0 |
Over-read character. Character sent out in case of an over-read of the transmit buffer. |
|
SHORTS
Address offset: 0x200
Shortcut register
| Bit number | 31 | 30 | 29 | 28 | 27 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 23 | 22 | 21 | 20 | 19 | 18 | 17 | 16 | 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Id | B | A | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reset 0x00000000 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Id | RW | Field | Value Id | Value | Description | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A | RW |
WRITE_SUSPEND |
Shortcut between WRITE event and SUSPEND task See EVENTS_WRITE and TASKS_SUSPEND |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Disabled |
0 |
Disable shortcut |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Enabled |
1 |
Enable shortcut |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| B | RW |
READ_SUSPEND |
Shortcut between READ event and SUSPEND task See EVENTS_READ and TASKS_SUSPEND |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Disabled |
0 |
Disable shortcut |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Enabled |
1 |
Enable shortcut |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
INTEN
Address offset: 0x300
Enable or disable interrupt
| Bit number | 31 | 30 | 29 | 28 | 27 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 23 | 22 | 21 | 20 | 19 | 18 | 17 | 16 | 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Id | H | G | F | E | B | A | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reset 0x00000000 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Id | RW | Field | Value Id | Value | Description | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A | RW |
STOPPED |
Enable or disable interrupt for STOPPED event See EVENTS_STOPPED |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Disabled |
0 |
Disable |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Enabled |
1 |
Enable |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| B | RW |
ERROR |
Enable or disable interrupt for ERROR event See EVENTS_ERROR |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Disabled |
0 |
Disable |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Enabled |
1 |
Enable |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| E | RW |
RXSTARTED |
Enable or disable interrupt for RXSTARTED event See EVENTS_RXSTARTED |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Disabled |
0 |
Disable |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Enabled |
1 |
Enable |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| F | RW |
TXSTARTED |
Enable or disable interrupt for TXSTARTED event See EVENTS_TXSTARTED |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Disabled |
0 |
Disable |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Enabled |
1 |
Enable |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| G | RW |
WRITE |
Enable or disable interrupt for WRITE event See EVENTS_WRITE |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Disabled |
0 |
Disable |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Enabled |
1 |
Enable |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| H | RW |
READ |
Enable or disable interrupt for READ event See EVENTS_READ |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Disabled |
0 |
Disable |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Enabled |
1 |
Enable |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
INTENSET
Address offset: 0x304
Enable interrupt
| Bit number | 31 | 30 | 29 | 28 | 27 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 23 | 22 | 21 | 20 | 19 | 18 | 17 | 16 | 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Id | H | G | F | E | B | A | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reset 0x00000000 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Id | RW | Field | Value Id | Value | Description | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A | RW |
STOPPED |
Write '1' to Enable interrupt for STOPPED event See EVENTS_STOPPED |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Set |
1 |
Enable |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Disabled |
0 |
Read: Disabled |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Enabled |
1 |
Read: Enabled |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| B | RW |
ERROR |
Write '1' to Enable interrupt for ERROR event See EVENTS_ERROR |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Set |
1 |
Enable |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Disabled |
0 |
Read: Disabled |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Enabled |
1 |
Read: Enabled |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| E | RW |
RXSTARTED |
Write '1' to Enable interrupt for RXSTARTED event See EVENTS_RXSTARTED |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Set |
1 |
Enable |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Disabled |
0 |
Read: Disabled |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Enabled |
1 |
Read: Enabled |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| F | RW |
TXSTARTED |
Write '1' to Enable interrupt for TXSTARTED event See EVENTS_TXSTARTED |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Set |
1 |
Enable |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Disabled |
0 |
Read: Disabled |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Enabled |
1 |
Read: Enabled |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| G | RW |
WRITE |
Write '1' to Enable interrupt for WRITE event See EVENTS_WRITE |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Set |
1 |
Enable |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Disabled |
0 |
Read: Disabled |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Enabled |
1 |
Read: Enabled |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| H | RW |
READ |
Write '1' to Enable interrupt for READ event See EVENTS_READ |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Set |
1 |
Enable |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Disabled |
0 |
Read: Disabled |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Enabled |
1 |
Read: Enabled |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
INTENCLR
Address offset: 0x308
Disable interrupt
| Bit number | 31 | 30 | 29 | 28 | 27 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 23 | 22 | 21 | 20 | 19 | 18 | 17 | 16 | 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Id | H | G | F | E | B | A | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reset 0x00000000 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Id | RW | Field | Value Id | Value | Description | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A | RW |
STOPPED |
Write '1' to Disable interrupt for STOPPED event See EVENTS_STOPPED |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Clear |
1 |
Disable |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Disabled |
0 |
Read: Disabled |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Enabled |
1 |
Read: Enabled |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| B | RW |
ERROR |
Write '1' to Disable interrupt for ERROR event See EVENTS_ERROR |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Clear |
1 |
Disable |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Disabled |
0 |
Read: Disabled |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Enabled |
1 |
Read: Enabled |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| E | RW |
RXSTARTED |
Write '1' to Disable interrupt for RXSTARTED event See EVENTS_RXSTARTED |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Clear |
1 |
Disable |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Disabled |
0 |
Read: Disabled |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Enabled |
1 |
Read: Enabled |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| F | RW |
TXSTARTED |
Write '1' to Disable interrupt for TXSTARTED event See EVENTS_TXSTARTED |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Clear |
1 |
Disable |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Disabled |
0 |
Read: Disabled |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Enabled |
1 |
Read: Enabled |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| G | RW |
WRITE |
Write '1' to Disable interrupt for WRITE event See EVENTS_WRITE |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Clear |
1 |
Disable |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Disabled |
0 |
Read: Disabled |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Enabled |
1 |
Read: Enabled |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| H | RW |
READ |
Write '1' to Disable interrupt for READ event See EVENTS_READ |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Clear |
1 |
Disable |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Disabled |
0 |
Read: Disabled |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Enabled |
1 |
Read: Enabled |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
ERRORSRC
Address offset: 0x4D0
Error source
| Bit number | 31 | 30 | 29 | 28 | 27 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 23 | 22 | 21 | 20 | 19 | 18 | 17 | 16 | 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Id | C | B | A | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reset 0x00000000 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Id | RW | Field | Value Id | Value | Description | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A | RW |
OVERFLOW |
RX buffer overflow detected, and prevented |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
NotDetected |
0 |
Error did not occur |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Detected |
1 |
Error occurred |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| B | RW |
DNACK |
NACK sent after receiving a data byte |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
NotReceived |
0 |
Error did not occur |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Received |
1 |
Error occurred |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| C | RW |
OVERREAD |
TX buffer over-read detected, and prevented |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
NotDetected |
0 |
Error did not occur |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Detected |
1 |
Error occurred |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
MATCH
Address offset: 0x4D4
Status register indicating which address had a match
| Bit number | 31 | 30 | 29 | 28 | 27 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 23 | 22 | 21 | 20 | 19 | 18 | 17 | 16 | 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Id | A | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reset 0x00000000 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Id | RW | Field | Value Id | Value | Description | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A | R |
MATCH |
[0..1] |
Which of the addresses in {ADDRESS} matched the incoming address |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
ENABLE
Address offset: 0x500
Enable TWIS
| Bit number | 31 | 30 | 29 | 28 | 27 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 23 | 22 | 21 | 20 | 19 | 18 | 17 | 16 | 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Id | A | A | A | A | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reset 0x00000000 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Id | RW | Field | Value Id | Value | Description | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A | RW |
ENABLE |
Enable or disable TWIS |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Disabled |
0 |
Disable TWIS |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Enabled |
9 |
Enable TWIS |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
PSEL.SCL
Address offset: 0x508
Pin select for SCL signal
| Bit number | 31 | 30 | 29 | 28 | 27 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 23 | 22 | 21 | 20 | 19 | 18 | 17 | 16 | 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Id | B | A | A | A | A | A | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reset 0xFFFFFFFF | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Id | RW | Field | Value Id | Value | Description | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A | RW |
PIN |
[0..31] |
Pin number |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| B | RW |
CONNECT |
Connection |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Disconnected |
1 |
Disconnect |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Connected |
0 |
Connect |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
PSEL.SDA
Address offset: 0x50C
Pin select for SDA signal
| Bit number | 31 | 30 | 29 | 28 | 27 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 23 | 22 | 21 | 20 | 19 | 18 | 17 | 16 | 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Id | B | A | A | A | A | A | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reset 0xFFFFFFFF | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |||
| Id | RW | Field | Value Id | Value | Description | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A | RW |
PIN |
[0..31] |
Pin number |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| B | RW |
CONNECT |
Connection |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Disconnected |
1 |
Disconnect |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Connected |
0 |
Connect |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
RXD.PTR
Address offset: 0x534
RXD Data pointer
| Bit number | 31 | 30 | 29 | 28 | 27 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 23 | 22 | 21 | 20 | 19 | 18 | 17 | 16 | 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Id | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | |||
| Reset 0x00000000 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Id | RW | Field | Value Id | Value | Description | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A | RW |
PTR |
RXD Data pointer |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
RXD.MAXCNT
Address offset: 0x538
Maximum number of bytes in RXD buffer
| Bit number | 31 | 30 | 29 | 28 | 27 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 23 | 22 | 21 | 20 | 19 | 18 | 17 | 16 | 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Id | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reset 0x00000000 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Id | RW | Field | Value Id | Value | Description | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A | RW |
MAXCNT |
Maximum number of bytes in RXD buffer |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
RXD.AMOUNT
Address offset: 0x53C
Number of bytes transferred in the last RXD transaction
| Bit number | 31 | 30 | 29 | 28 | 27 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 23 | 22 | 21 | 20 | 19 | 18 | 17 | 16 | 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Id | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reset 0x00000000 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Id | RW | Field | Value Id | Value | Description | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A | R |
AMOUNT |
Number of bytes transferred in the last RXD transaction |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
TXD.PTR
Address offset: 0x544
TXD Data pointer
| Bit number | 31 | 30 | 29 | 28 | 27 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 23 | 22 | 21 | 20 | 19 | 18 | 17 | 16 | 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Id | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | |||
| Reset 0x00000000 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Id | RW | Field | Value Id | Value | Description | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A | RW |
PTR |
TXD Data pointer |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
TXD.MAXCNT
Address offset: 0x548
Maximum number of bytes in TXD buffer
| Bit number | 31 | 30 | 29 | 28 | 27 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 23 | 22 | 21 | 20 | 19 | 18 | 17 | 16 | 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Id | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reset 0x00000000 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Id | RW | Field | Value Id | Value | Description | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A | RW |
MAXCNT |
Maximum number of bytes in TXD buffer |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
TXD.AMOUNT
Address offset: 0x54C
Number of bytes transferred in the last TXD transaction
| Bit number | 31 | 30 | 29 | 28 | 27 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 23 | 22 | 21 | 20 | 19 | 18 | 17 | 16 | 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Id | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reset 0x00000000 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Id | RW | Field | Value Id | Value | Description | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A | R |
AMOUNT |
Number of bytes transferred in the last TXD transaction |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
ADDRESS[0]
Address offset: 0x588
TWI slave address 0
| Bit number | 31 | 30 | 29 | 28 | 27 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 23 | 22 | 21 | 20 | 19 | 18 | 17 | 16 | 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Id | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reset 0x00000000 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Id | RW | Field | Value Id | Value | Description | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A | RW |
ADDRESS |
TWI slave address |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
ADDRESS[1]
Address offset: 0x58C
TWI slave address 1
| Bit number | 31 | 30 | 29 | 28 | 27 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 23 | 22 | 21 | 20 | 19 | 18 | 17 | 16 | 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Id | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reset 0x00000000 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Id | RW | Field | Value Id | Value | Description | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A | RW |
ADDRESS |
TWI slave address |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
CONFIG
Address offset: 0x594
Configuration register for the address match mechanism
| Bit number | 31 | 30 | 29 | 28 | 27 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 23 | 22 | 21 | 20 | 19 | 18 | 17 | 16 | 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Id | B | A | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reset 0x00000001 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | |||
| Id | RW | Field | Value Id | Value | Description | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A | RW |
ADDRESS0 |
Enable or disable address matching on ADDRESS[0] |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Disabled |
0 |
Disabled |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Enabled |
1 |
Enabled |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| B | RW |
ADDRESS1 |
Enable or disable address matching on ADDRESS[1] |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Disabled |
0 |
Disabled |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Enabled |
1 |
Enabled |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
ORC
Address offset: 0x5C0
Over-read character. Character sent out in case of an over-read of the transmit buffer.
| Bit number | 31 | 30 | 29 | 28 | 27 | 26 | 25 | 24 | 23 | 22 | 21 | 20 | 19 | 18 | 17 | 16 | 15 | 14 | 13 | 12 | 11 | 10 | 9 | 8 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 0 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Id | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | A | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Reset 0x00000000 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |||
| Id | RW | Field | Value Id | Value | Description | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| A | RW |
ORC |
Over-read character. Character sent out in case of an over-read of the transmit buffer. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Electrical specification
TWIS slave interface electrical specifications
| Symbol | Description | Min. | Typ. | Max. | Units | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| fTWIS |
Bit rates for TWIS1 |
100 | 400 | kbps | |||||
| ITWIS,100kbps |
Run current for TWIS (Average current to receive and transfer a byte to RAM), 100 kbps |
45 | µA | ||||||
| ITWIS,400kbps |
Run current for TWIS (Average current to receive and transfer a byte to RAM), 400 kbps |
45 | µA | ||||||
| ITWIS,IDLE |
Idle current for TWIS |
1 | µA | ||||||
| tTWIS,START,LP |
Time from PREPARERX/PREPARETX task to ready to receive/transmit, Low power mode |
tTWIS,START,CL + tSTART_HFINT | µs | ||||||
| tTWIS,START,CL |
Time from PREPARERX/PREPARETX task to ready to receive/transmit, Constant latency mode |
1.5 | µs |
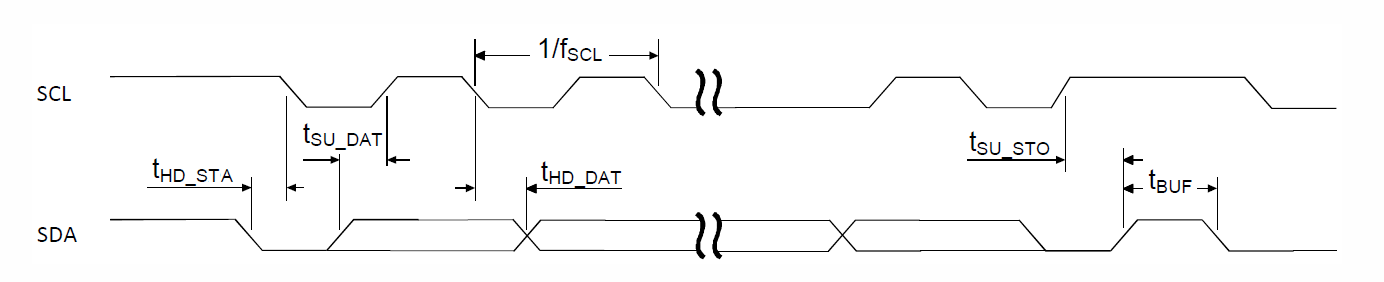
TWIS slave timing specifications
| Symbol | Description | Min. | Typ. | Max. | Units | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| fTWIS,SCL,400kbps |
SCL clock frequency, 400 kbps |
400 | kHz | ||||||
| tTWIS,SU_DAT |
Data setup time before positive edge on SCL – all modes |
300 | ns | ||||||
| tTWIS,HD_DAT |
Data hold time after negative edge on SCL – all modes |
500 | ns | ||||||
| tTWIS,HD_STA,100kbps |
TWI slave hold time from for START condition (SDA low to SCL low), 100 kbps |
5200 | ns | ||||||
| tTWIS,HD_STA,400kbps |
TWI slave hold time from for START condition (SDA low to SCL low), 400 kbps |
1300 | ns | ||||||
| tTWIS,SU_STO,100kbps |
TWI slave setup time from SCL high to STOP condition, 100 kbps |
5200 | ns | ||||||
| tTWIS,SU_STO,400kbps |
TWI slave setup time from SCL high to STOP condition, 400 kbps |
1300 | ns | ||||||
| tTWIS,BUF,100kbps |
TWI slave bus free time between STOP and START conditions, 100 kbps |
4700 | ns | ||||||
| tTWIS,BUF,400kbps |
TWI slave bus free time between STOP and START conditions, 400 kbps |
1300 | ns |