The nRF System-on-Chip supports multiple radio protocols. Applications running on the nRF SoC can use several radio protocols, but only one at a time. You can implement concurrency as either switched multiprotocol or dynamic multiprotocol.
Switched multiprotocol
The switched multiprotocol solution is the simplest one. This method requires disabling the currently used protocol before enabling another one, and thus achieving non-concurrent radio access.
During the initialization procedure, a switched multiprotocol application switches on one selected protocol (e.g. BLE). Prior to enabling another protocol (e.g. Thread), the application switches off the previously enabled protocol. The drawback of this solution is breaking all BLE connections when enabling Thread, and breaking all Thread connections when enabling BLE. In addition, the switching period is significantly higher than in the dynamic multiprotocol method, since it involves uninitialization of the current protocol and initialization of another one from scratch.
When a node enables the Thread protocol, it attaches to the Thread mesh network. The attachment procedure can take between 0.2 and 5 seconds (these numbers result from protocol specification, depend on the network topology, and randomly chosen delays, and thus cannot be fully determined). When a node attaches to the network, it can immediately start transmitting/receiving data to/from other nodes. In the other direction, when a node enables BLE protocol and operates e.g. as a BLE Peripheral, it has to start advertising and wait for a BLE connection.
In the switched multiprotocol method, switching between different protocols is usually performed by an application in appropriate user-defined moments. For example, a node may advertise on BLE and wait for a connection. After the connection is established and the node receives some application data e.g. over GATT, it may uninitialize the BLE stack and enable the Thread stack. After the attachment to a mesh network is successful, the node may push previously obtained data into the cloud using native IPv6 protocols and switch back to BLE.
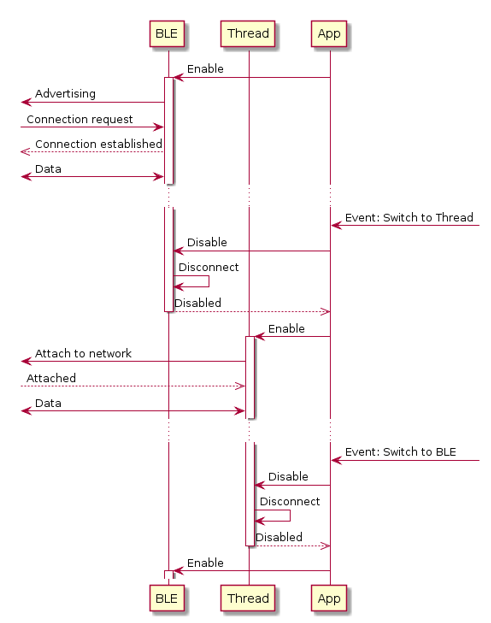
Switched multiprotocol examples are provided in this release of nRF5 SDK for Thread.
Switched multiprotocol – timings
The overall switching timings between BLE and Thread may vary in different applications. The figure below presents the switching timings measured on the Switched BLE-Thread Template Example.
The procedure of switching from BLE to Thread and back to BLE consists of the following steps:
| # | Phase name | Description | Timing measurements |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | BLE transactions | device operates on BLE protocol | Application specific |
| 2 | BLE stack disable | device disables SoftDevice | 233-260 [us] softdevice_handler_sd_disable() |
| 3 | Thread stack enable | device enables OpenThread stack | ~33 [ms] PlatformInit() otInstanceInit() otIp6SetEnabled() otThreadSetEnabled() |
| 4 | Thread attaching | device attaches to the Thread network | 0.2 – 5 [s] Time is highly non-deterministic and may depend on the current network role, air traffic, random jitters, or other non-deterministic factors defined in the Thread protocol. |
| 5 | Thread transactions | device operates on Thread protocol | Application specific |
| 6 | Thread stack disable | device disables OpenThread stack | 490 – 530 [us] otInstanceFinalize() PlatformDeinit() |
| 7 | BLE stack enable | device enables SoftDevice | ~251 [ms] SOFTDEVICE_HANDLER_INIT() sd_ble_cfg_set() softdevice_enable() softdevice_ble_evt_handler_set() softdevice_sys_evt_handler_set() |
| 8 | BLE initialization | for example, GATT services initialization | Application specific |
| 9 | BLE transactions | device operates on BLE protocol | Application specific |
Dynamic multiprotocol
- Note
- Dynamic multiprotocol examples are not provided in this release of nRF5 SDK for Thread.
The dynamic multiprotocol solution allows for running several radio protocols simultaneously without the time-expensive uninitialization and initialization in-between the switching. Radio hardware is time-sliced between all protocols. Each radio protocol (BLE or Thread) requests a time slot prior to any radio operation. This solution allows for keeping established connections in a few protocols at the same time. Transmitting and receiving data does not break connections from any of the used radio protocols. This method requires concurrent (time-multiplex) radio access.
The figure below shows how Thread and BLE protocols operate in the dynamic multiprotocol mode.
In the dynamic multiprotocol method, switching between different protocols is done automatically in the background of the currently running application. Switching between protocols requires only a reinitialization of the radio peripheral, since protocols may operate on different frequencies, modulations etc. Therefore, the time of switching is much shorter than in the switched multiprotocol method. In addition, as in the given example, both connections on Thread and BLE may be maintained without disconnecting the other one.
Note that in case of Thread protocol, some radio packets may be lost due to the BLE activity. Thus, BLE timings such as advertising interval or connection interval should be long enough to fit Thread operations in between. Also, the Thread Router should keep its receiver switched on all the time when it does not transmit, which demands from it to make the best effort to operate on the 802.15.4 link as often as possible, without affecting BLE connectivity.
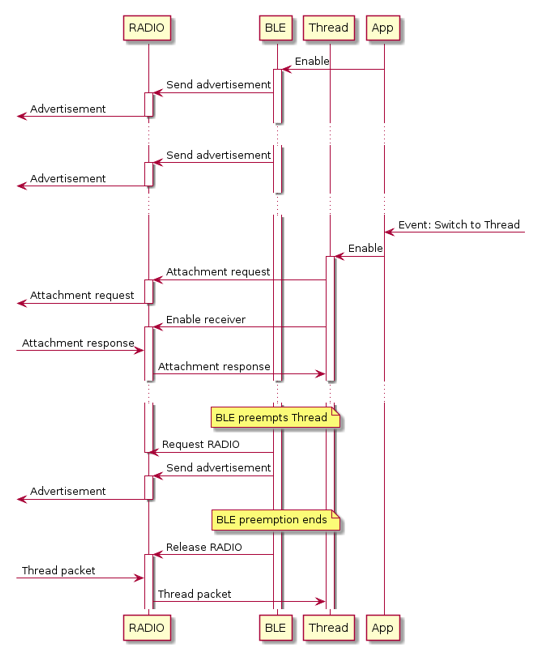
The dynamic multiprotocol examples will be provided in the upcoming releases of nRF5 SDK for Thread.
Multiprotocol examples
nRF5 SDK for Thread provides the following applications that show how multiprotocol support for BLE and Thread can be implemented:
A Dynamic Multiprotocol BLE-Thread Example will be released soon.