nRF5 SDK for Thread is intended for use with the nRF52840 Development Kit.
The SDK provides the precompiled OpenThread library. The library was built on Linux with arm-none-eabi-gcc version 6.3.0 with the following parameters:
OpenThread is natively developed in POSIX environment, and it is a recommended setup to build and test the Thread SDK examples. However, it is possible to build the examples on Windows with the MinGW environment. If you have already built regular nRF5 SDK examples with the GCC compiler on you machine, you should be able to build Thread examples as well, without additional effort.
The following peripherals are owned by the OpenThread stack and cannot be used directly by an application:
- RTC2
- UART0
- RADIO
- RNG
- CRYPTOCELL
OpenThread API can be used to access the hardware random number generator.
Environment setup
You must install a set of tools to complete the environment setup process.
Linux
Make
First, make sure that you have the make tool installed on your system. To do this, run the following command:
If the command does not provide output, you must install the make tool. Refer to the documentation of your Linux distribution for information on how to download and install it.
GNU ARM Embedded Toolchain
To be able to compile projects for the nRF52840 Development Kit, you must install GNU ARM Embedded Toolchain in version 4.9.3. You can download this version from GNU ARM Embedded Toolchain. Make sure to install it in the /usr/local/gcc-arm-none-eabi-4_9-2015q3 folder.
If you already have another version of arm-none-eabi installed, you can modify the default path in the following file: <InstallFolder>/components/toolchain/gcc/Makefile.posix.
SEGGER J-Link
To enable communication between devices, you need the SEGGER J-Link utility. Recommended version is 6.14d, which can be downloaded from J-Link Download page.
- Note
- Due to a known issue in Segger’s J-Link firmware, depending on your operating system and version, you might experience data corruption or drops if you use the serial port. You can avoid this issue by disabling the Mass Storage Device:
- On Linux or macOS (OS X), open JLinkExe from the terminal. On Microsoft Windows, open the J-Link Commander application.
- Run the following command: MSDDisable
nrfjprog
You need the nrfjprog tool to program the nRF52840 chips. The latest version of this tool can be found on the nRF52840 product website.
Windows
Make
The make tool, required to build GCC projects, is not natively available on Windows. However, the MinGW package can be used to install it:
- Download the MinGW installer. The 32-bit version is recommended.
- Run the downloaded binary and select a folder where the MinGW toolchain will be installed. The recommended path is
C:\MinGW - When the first part of the installation is finished, the MinGW Installation Manager opens.
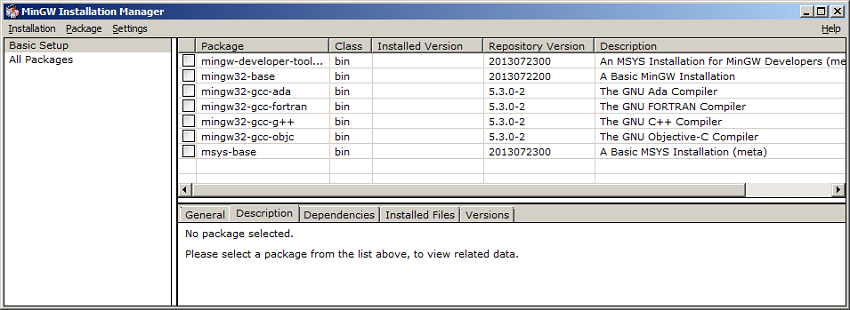 MinGW Installation Manager
MinGW Installation Manager
- From the package list, select mingw32-base and msys-base. Then, click Installation -> Apply changes to install the selected items.
- Add the following paths to the PATH variable in your system:
C:\MinGW\binC:\MinGW\msys\1.0\bin
To do so, right-click My computer, select Properties -> Advanced system settings -> Environment Variables and double-click the PATH variable. Then, append the existing string with the two paths, each preceded by a semicolon, for example:System reboot might be required for the new paths to work properly.…; C:\MinGW\bin;C:\MinGW\msys\1.0\bin
- After the installation process finishes, open the command prompt and verify that it succeeded. To do this, check that the Msys environment was set up correctly by running the following command: You should receive the following result:uname -–operating-system
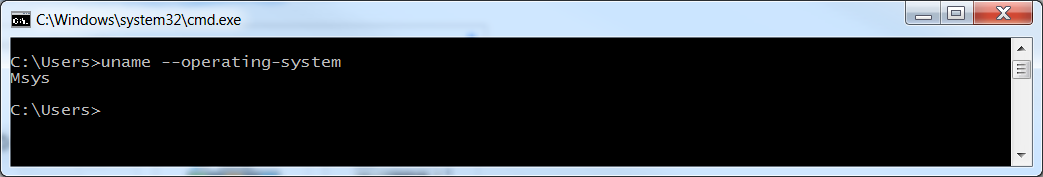 System information
System information - Additionally, check that the
maketool was installed correctly by typingmake --versionand pressing Enter. If there are no errors during installation, the following message is displayed:GNU ARM Embedded Toolchain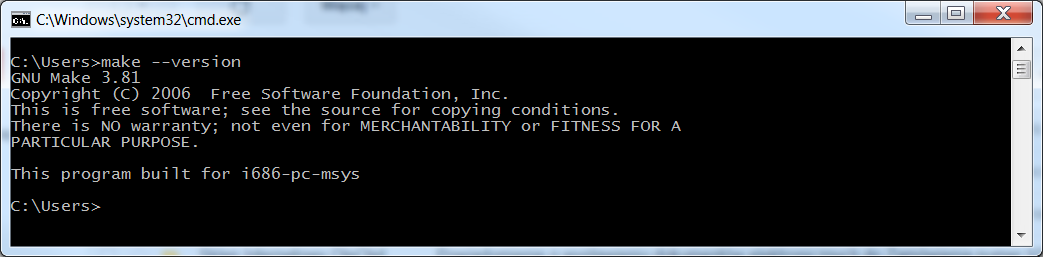 Version information
Version information
To be able to compile projects for the nRF52840 Development Kit, you must install GNU ARM Embedded Toolchain in version 4.9.3. You can download this version from GNU ARM Embedded Toolchain. It is recommended to install it in the default directory: C:\Program Files (x86)\GNU Tools ARM Embedded\4.9 2015q3.
If you already have another version of arm-none-eabi installed, or have installed it in a different directory, you can modify the default path in the following file: <InstallFolder>\components\toolchain\gcc\Makefile.windows.
nRF5x Command Line Tools
To communicate with and program the nRF52840 Development Kit, you need the SEGGER J-Link and nrfjprog tools. Download and install the latest version of nRF5x Command Line Tools from the nRF52840 product website. This package includes the latest version of SEGGER J-Link and nrfjprog utilities.
After the installation is complete, add nrfjprog installation directory (for example C:\Program Files (x86)\Nordic Semiconductor\nrf5x\bin\) to your system PATH variable.
- Note
- If you experience communication issues with the nRF52840 Development Kit, it is recommended to update SEGGER J-Link to version 6.14d. To do so, uninstall the current version of SEGGER J-Link, and then install the recommended version manually. The installer can be found on the J-Link Download page.
Building and running examples
Building an example
To build an example, perform the following steps:
- Open Windows command line or Linux terminal.
- Navigate to the selected example folder, and then to the armgcc project directory, for example:
<InstallFolder>/examples/thread/experimental/cli/pca10056/blank/armgcc. - Run the
makecommand in this folder. If the environment was set up correctly, the build process will start. - The build process produces the HEX file inside the
_buildfolder:<InstallFolder>/examples/thread/experimental/cli/pca10056/blank/armgcc/_build/nrf52840_xxaa.hex.- Note
- If you experience difficulties when running the
makecommand on Windows, make sure that you do not have any othermakeinstances from other toolsets like Cygwin or GnuWin32 in your PATH variable.
Running an example
To program the nRF52840 Development Kit, first connect it to your computer with a USB cable. When your board is detected, type the following commands:
- To program the device, run: nrfjprog -f NRF52 --chiperase --program _build/nrf52840.hex
- To reset the device, run: For a list of available nrfjprog commands, run:nrfjprog -rnrfjprog --help
You can use RTT Viewer to view the log messages produced by the example.
Building the latest OpenThread libraries
It is recommended to use the provided, precompiled version of the OpenThread library. However, it is possible to compile the latest version from GitHub. Currently, only the POSIX environment is supported, so you need Linux or Mac to build the OpenThread library.
- Note
- Support for hardware-accelerated cryptography utilizing ARM CryptoCell-310 is only available in mbedTLS library (
libmbedcrypto.a) provided with the SDK. The library available in OpenThread repository does not support hardware acceleration. You can still use it, but the commissioning procedure takes more time in such case (see table for comparison). For the best performance, use the library provided with the SDK.Version Commissioning (with Network Discovery) DTLS Handshake Without CryptoCell 37,76 s 32,88 s With CryptoCell 6,31 s 1,51 s
Follow these steps to build the library:
- Make sure you have GNU Autotools installed on your system. Refer to the documentation of your distribution for information on how to download and install them.
- Download or clone the OpenThread stack repository.
- Navigate into the repository root folder.
- Run the following commands: You can experiment with the build parameters, but make sure you include the parameters presented above. Otherwise, some examples might not compile or work properly. To create libraries suitable for performing Thread certification tests, run$ ./bootstrap$ make –f examples/Makefile-nrf52840 COAP=1 COMMISSIONER=1 JOINER=1 DNS_CLIENT=1
makewith the following parameters:$ make –f examples/Makefile-nrf52840 COMMISSIONER=1 JOINER=1 DHCP6_SERVER=1 DHCP6_CLIENT=1 CERT_LOG=1 DEFAULT_LOGGING=1 COAP=1 - Copy the libraries from
<OpenThreadFolder>/output/libto the SDK folder:/external/openthread/lib/gcc. Do not overwrite thelibmbedcrypto.alibrary if you want to use hardware accelerator for cryptographic operations. - Copy the
<OpenThreadFolder>/includefolder into the/external/openthreadfolder. - Now, you can recompile the examples with the latest libraries.
- Note
- OpenThread is still in prerelease phase and its API changes frequently. Keep in mind that when the API changes, the examples might not compile with the latest OpenThread version right away without fixes.
Building mbedTLS library with CryptoCell support
If you want to update the mbedTLS library with CryptoCell support, for example when OpenThread updates the mbedTLS version it uses, you can build the new library within SDK.
To build the new library, perform the following steps:
- Manually update the mbedTLS source files in
<InstallFolder>/external/mbedtls. - Navigate to the
<InstallFolder>/components/thread/experimental/crypto/lib_nrf52/armgccfolder. - Run
maketo build the library. - Copy the
libmbedcrypto.alibrary into the OpenThread folder:<InstallFolder>/external/openthread/lib/gcc.
More information
See the following topics for further introduction into Nordic Semiconductor's Thread implementation.