nRF Thread Topology Monitor is a desktop application that helps to visualize the current network topology. The application requires a serial connection to an nRF52840 Development Kit with Nordic’s Thread solution.
Supported devices:
- nRF52840 Preview Development Kit
Supported operating systems:
- Windows 7, 8, and 10
- Ubuntu Linux 14.04 and 16.04
Installation
In Windows, it is required to install nRF Command Line Tools, which include the SEGGER J-Link software. See nRF5x Command Line Tools. In Linux, it is required to install the SEGGER J-Link software. If you do not have it installed already, download and install the software from J-Link Download page or from your distrubution package manager.
Follow these steps to install nRF Thread Topology Monitor:
- Navigate to nRF5 SDK for Thread web page and download the following package:
nRF_TTM-win32-x64_v0.11.0-1.alpha(for Windows) ornRF_TTM-linux-x64_v0.11.0-1.alpha.tar.gz(for Linux). - Extract the package suitable for the operating system that you are using.
- Run the nRF Thread Topology Monitor executable file to start the application.
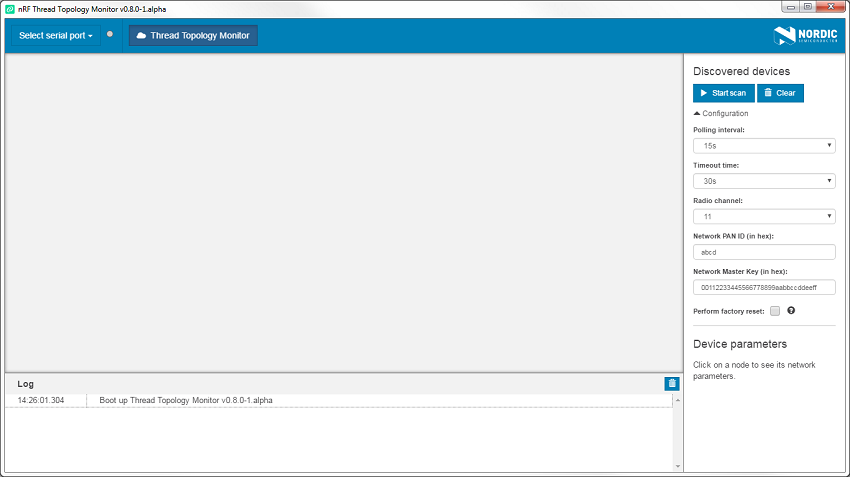
After starting nRF Thread Topology Monitor, you will see the main window of the application. It consists of the following elements:
- The area in the center is initially empty, but will be later populated with visual representations of Thread nodes.
- Navigation bar at the top that lets you select a serial port.
- Discovered Devices pane on the right contains options that let you scan the network or to clear the current topology view.
- Log area at the bottom of the screen which displays the most important log events, tagged with a timestamp.
Viewing network topology
nRF Thread Topology Monitor requires a serial port connection to a local nRF52840 Development Kit. The nRF SoC on the development kit is controlled by nRF Thread Topology Monitor which sends OpenThread CLI commands to it over serial port. Therefore, it must be programmed using the OpenThread CLI example.
Note that nRF Thread Topology Monitor filters serial ports to show only those with J-Link support. Therefore, only nRF52840 Development Kits that are communicated over J-Link UART can be used with the application.
Follow these steps to set up a local device:
- Connect a development kit to the computer via USB.
- Use nrfjprog (from nRF5x Command Line Tools v9.2.0 or newer) to flash the nRF SoC with the OpenThread CLI example: nrfjprog -f NRF52 --program <InstallFolder>/examples/thread/cli/uart/hex/thread_cli_pca10056.hex --chiperasenrfjprog -f NRF52 -r
- In the navigation bar, click Select serial port.
- Select the serial port with the device that you want to use.
- Note
- When the serial port is selected, the Select serial port menu shows the name of the selected port.
- Click Start scan to attach the nRF SoC to the Thread network and to start polling nodes to get information on the current topology. nRF Thread Topology Monitor will start to communicate with a node using OpenThread serial CLI. After a couple of seconds, topology of the Thread network will appear in the central area of the application.
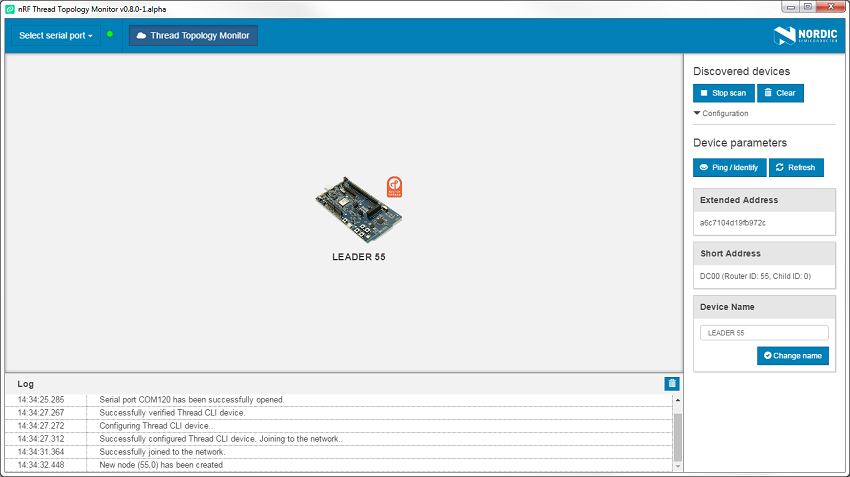
If the nRF SoC is the first Thread device in the network, it will become a Leader, as shown in the figure below.
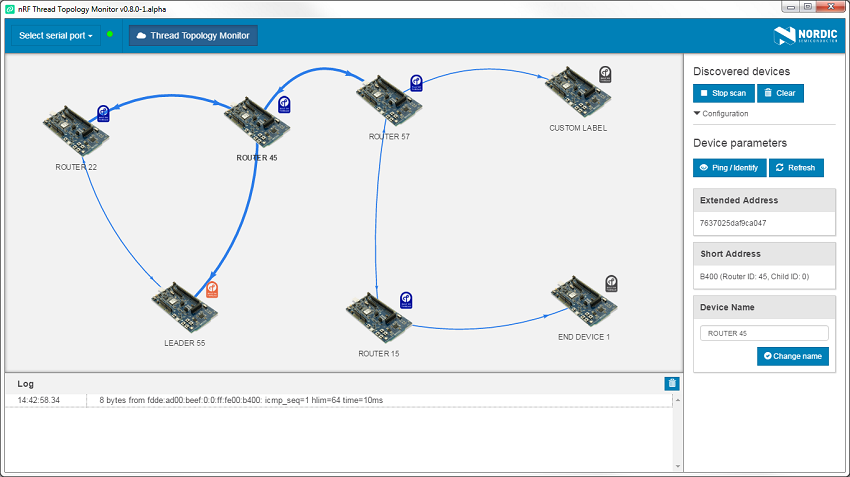
After other Thread devices have been attached to the network, nRF Thread Topology Monitor will visualize them as shown in the figure below.
- Note
- Click a Thread device to show its parameters.
- Use the mouse scroll to zoom in and zoom out of the network topology.
Configuration
The panel to the right of the main application window contains a Configuration section. Because nRF SoC acts as an OpenThread CLI device, you must configure the basic Operational Dataset. During this configuration, you can specify the following parameters of the Thread Network:
- Radio channel (11-26)
- Network PAN ID (e.g. abcd for 0xabcd)
- Network Master Key (e.g. 00112233445566778899aabbccddeeff)
- Select the Perform factory reset option to use a factory reset before the attachment process or to use normal reset otherwise.
- Note
- If a Thread node has already been commissioned with different parameters, such as Network PAN ID or Radio Channel, and the factory reset option is not selected, the configuration will not have any effect.
Apart from Thread network configuration, you can also specify two parameters related to polling: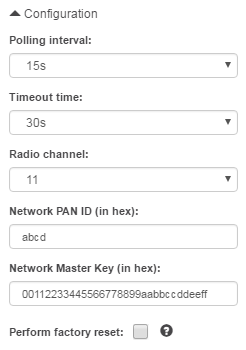 Configuration wizard
Configuration wizard
- Polling interval specifies how often the nRF SoC will poll other nodes for information about their status. It is recommended to keep the polling interval bigger (in seconds) than the total number of routers in the network.
- Timeout time specifies the maximum time span between two responses to poll requests, after which the node will be removed from the network topology.
Interacting with nodes
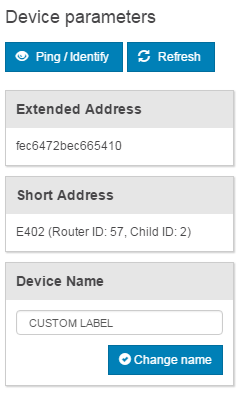
nRF Thread Topology Monitor allows to select a specific node in a Thread network and perform operations on it:
- Read its Extended and Short Addresses.
- Click Ping / Identify to ping the Thread device. If the Thread device uses the Thread BSP module, as do all examples in the
threaddirectory of this SDK, LEDs on this device will start blinking. - Click Refresh to refresh information about the device before regular polling.
- Change the device name. Note that nRF Thread Topology Monitor matches Extended Address with Device Name and stores it in persistent memory on the PC side.
Principle of operation
The background process of nRF Thread Topology Monitor communicates with nRF SoC using OpenThread CLI, sending commands described in OpenThread CLI Reference.
The application first attaches the nRF SoC to the network and then periodically retrieves the current list of routers. Each router is polled by sending the standard Thread diagnostic messages (MGMT_DIAG.req). In response, routers in the network send their current link set (current connected neighbors), child table, and basic network parameters, such as Network Address or Extended MAC Address.
Troubleshooting
An nRF Thread device does not change its Radio Channel/PAN ID/Master Key.
Thread parameters listed above are a part of Operational Dataset that can be changed only after factory reset. Make sure to check the Perform factory reset checkbox to change these network parameters.
A node in the Thread network changed its name to a default one, even after I set a custom label.
Thread protocol randomly chooses a new Extended Address on the Perform factory reset procedure. Therefore, the application cannot match its Extended Address with the previously assigned label.
After being a Thread Leader, I restarted the application with the Perform factory reset checkbox checked. Now I cannot see the topology.
nRF Thread device connected to the Thread Topology Monitor has to become a Thread Router to obtain all routing information. In Thread protocol, only the Leader of the network can allow a child to become a Thread Router. If the Leader has been restarted and some other Thread Routers exist in the network, they need to time out the previous Leader and elect a new one. This procedure may take up to two minutes.
nRF Thread Topology Monitor shows the Cannot open /dev/ttyACM0: Permission denied log under Linux OS.
The user does not have sufficient permissions to access the /dev/ttyACM0 serial port. You must add the current user to a proper group and log out to refresh the user credentials. The group name is distibution-dependent and in order to read it, run the following command:
ls -l /dev/ttyACM0For example, on the Ubuntu distribution, the group name is dialout.
sudo adduser USERNAME dialout
nRF Thread Topology Monitor shows the EACCES: permission denied, open '/home/USERNAME/.config/nRF_TTM/storage/commdataset.json' log under Linux OS.
The user does not have sufficient permissions to access storage files that keep information like the last configuration and node names. nRF_TTM might have been run with sudo permissions for the first time and now the application is run without them.
sudo chown -hR USERNAME /home/USERNAME/.config/nRF_TTM/